Process + Partnership. Top businesses from coast to coast trust AeroDynamics for their metal finishing needs
We understand the importance of precision plating as it relates to critical aspects of form, fit, and function. We work closely with you to engineer customized processes for your first articles and prototypes.
Our masking expertise includes the use of wet spray, wax, lacquer, paint, industry proven tapes, and a variety of different plugs individually designed for your application. These techniques are employed by trained masking specialists dedicated exclusively to your program.
Our racking & tooling proficiency allows us to develop customized solutions to any racking & tooling challenges. We use quality materials tailored to ensure that our plating process meets the requirements of your drawings.
Our close relationship with our vendors guarantees that our chemistries and equipment are correctly monitored and upgraded to meet modern advances within the industry.
We are open to working with all customers to plan and provide any processes that may or may not be currently offered by AeroDynamics. We thrive on the challenge of developing effective solutions for our customers and understand our vital position within their supply chain.
*AeroDynamics also complies with MIL-S-5002, MIL-STD-171, MIL-DTL-14072 standards
For more product development & process planning information
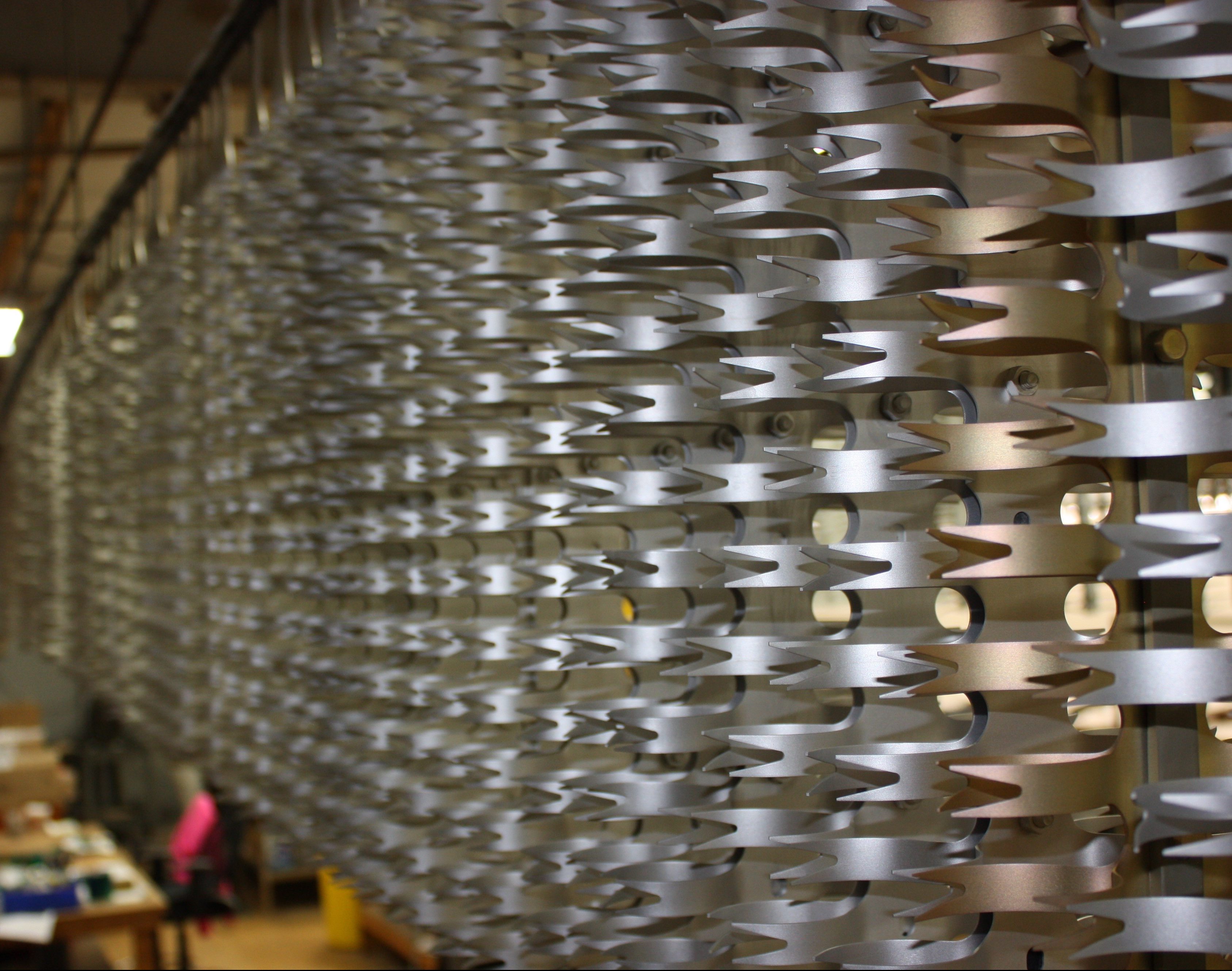
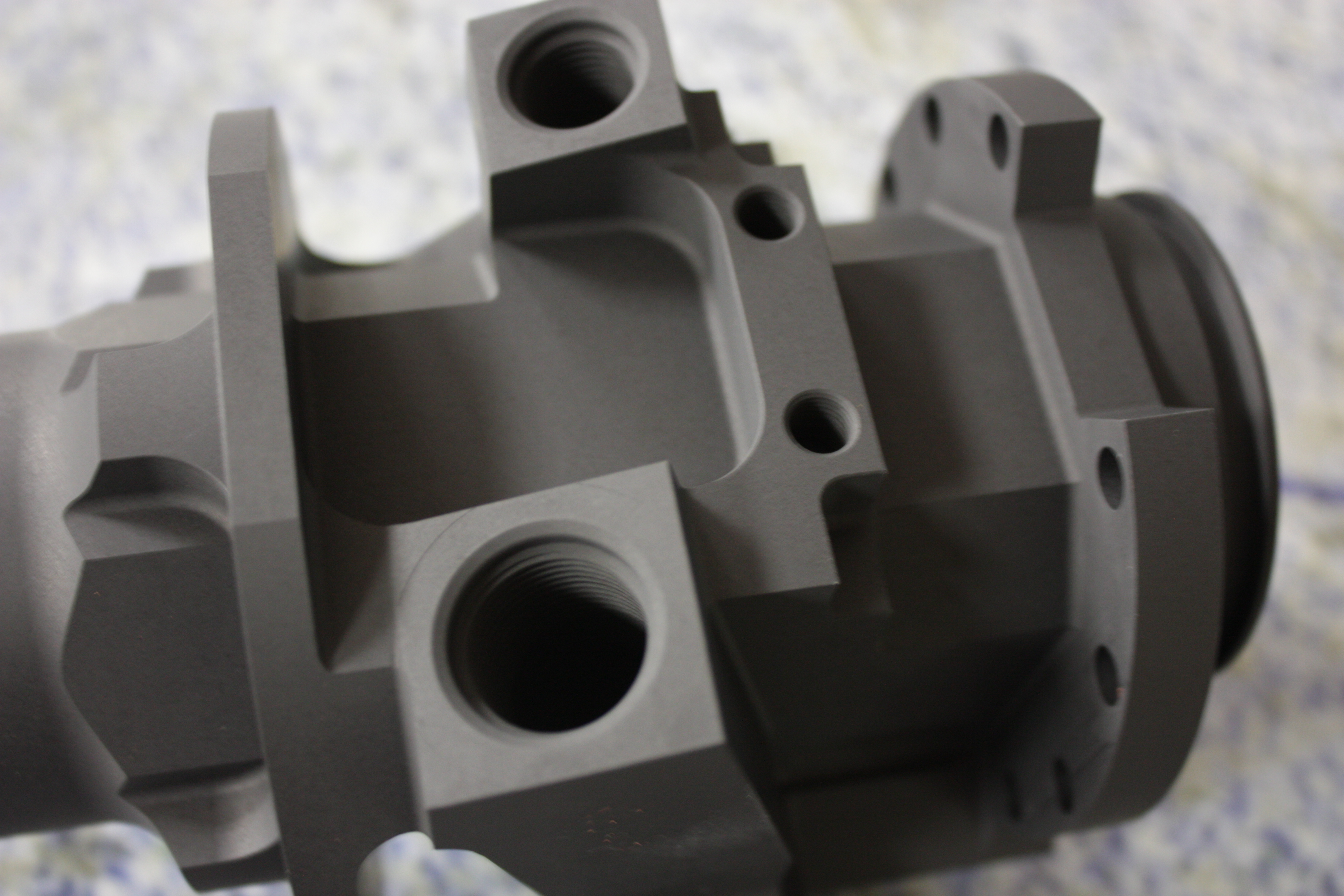
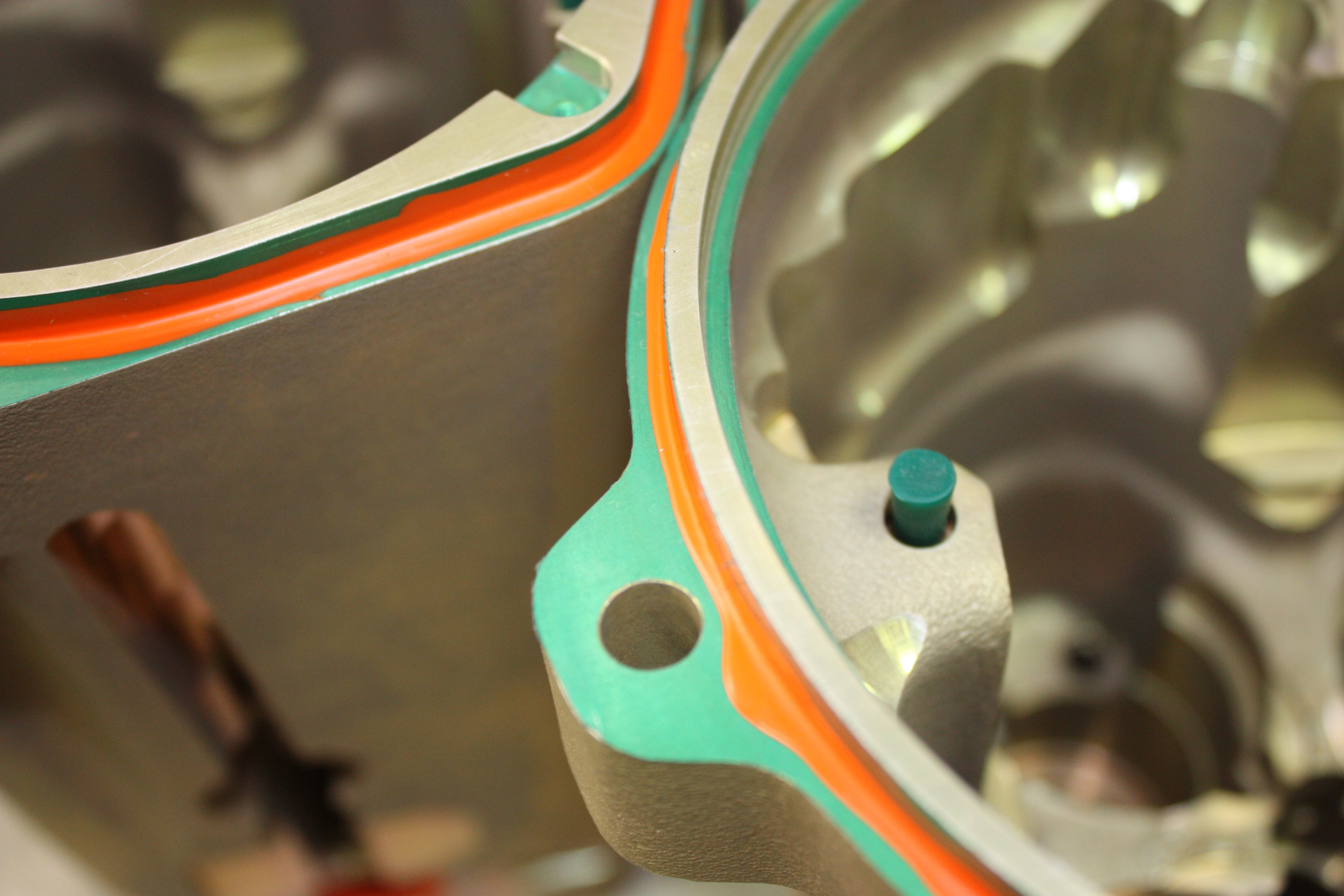

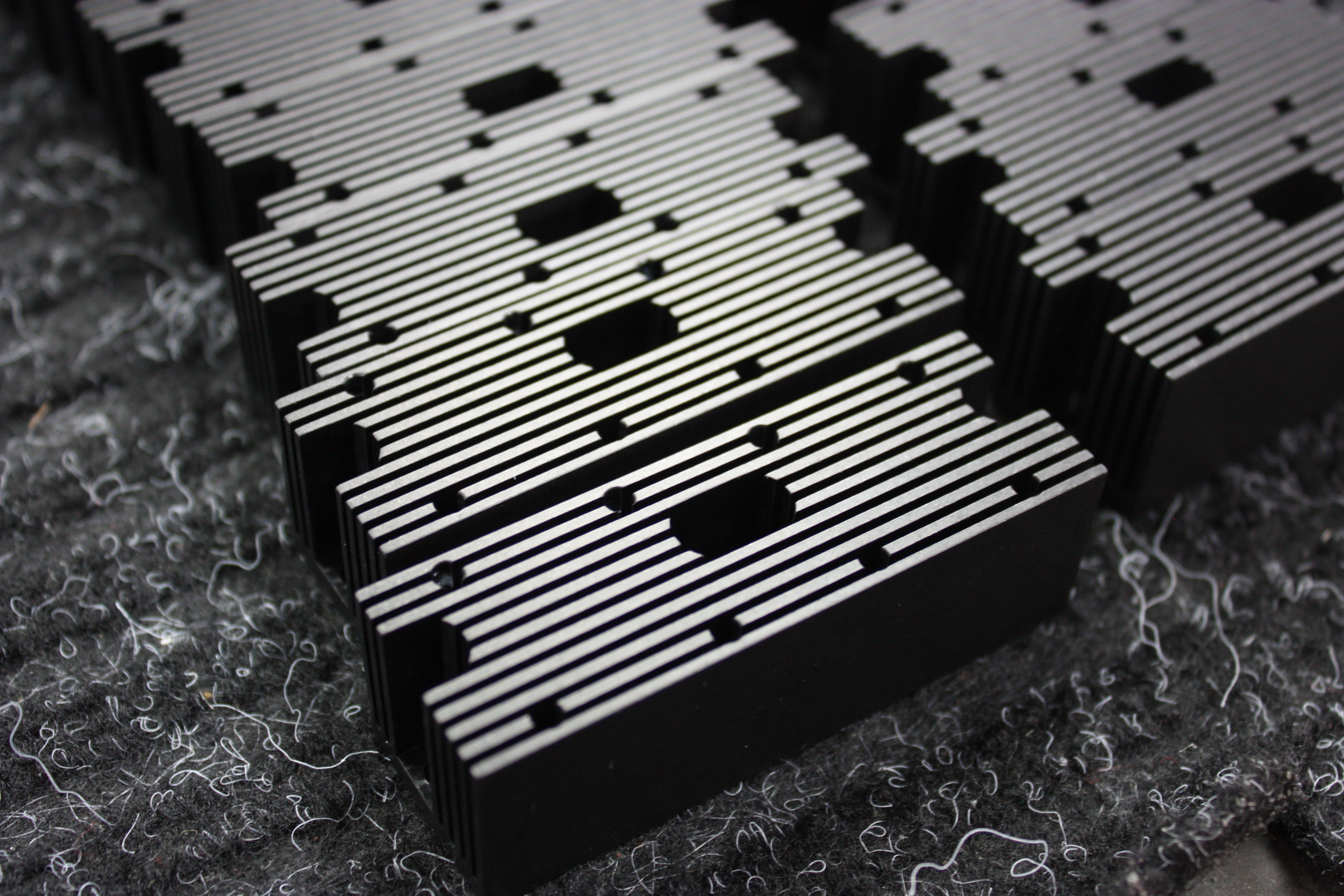

Anodize
Anodizing of aluminum is an electrolytic process used to increase the thickness and hardness of the natural aluminum oxide surface layer. This porous oxide is able to absorb and accept dye pigments to alter the aesthetics or other impregnations such as PTFE, commonly known as Teflon, which increases lubricity and wear resistance.
- Corrosion resistance
- Increased hardness
- Wear resistance
- Improved lubricity
For more anodizing information
Specifications
Type II: Sulfuric acid anodize
Type IIB: Thin sulfuric acid anodize
Type III: Hard anodic Coatings
Class 2: Dyed
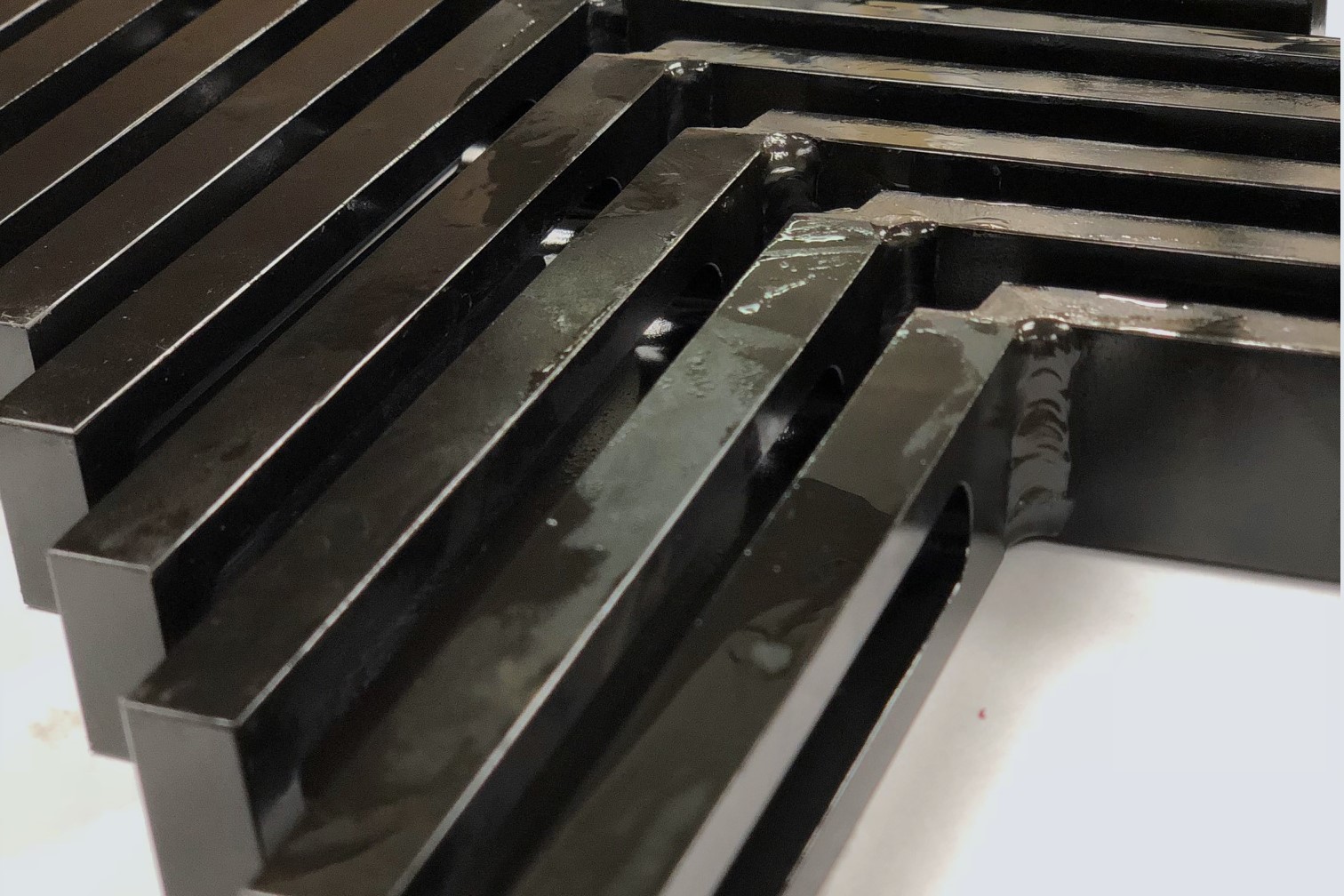
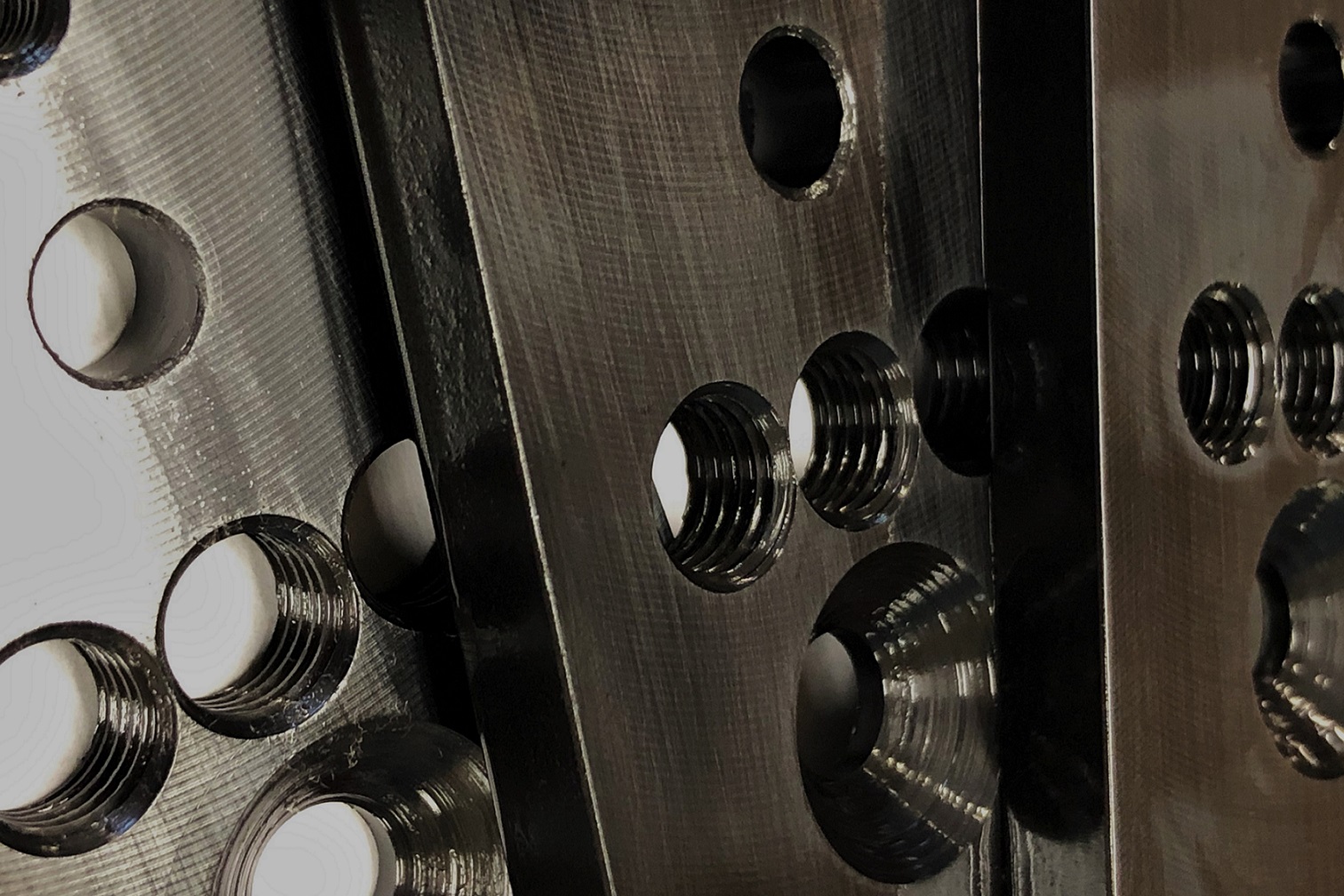


Black Oxide
Black oxide or blackening is a conversion coating for ferrous alloys. Blackening is a high-temperature alkaline oxidizing process that converts the surface of the substrate to a passive, porous oxide layer. Supplementary treatment with oil is typically applied to further increase corrosion resistance. Black oxide coatings are generally applied to materials to blacken the surface, minimize light reflection, provide mild corrosion resistance, and to improve lubricity with no dimensional impact.
- Reduce light reflection
- Mild corrosion resistance
- Improved lubricity
- No dimensional impact
For more black oxide information
Specifications
Class 1: Alkaline oxidizing process (for wrought iron, cast and malleable irons, plain carbon, and low alloy steels)
Class 4: Alkaline oxidizing process (for 300 series corrosion resistant steel alloys only)
Class 1: Alkaline oxidizing process (for wrought iron, cast and malleable irons, plain carbon, and low alloy steels)
Class 4: Alkaline oxidizing process (for other corrosion resistant steel alloys)
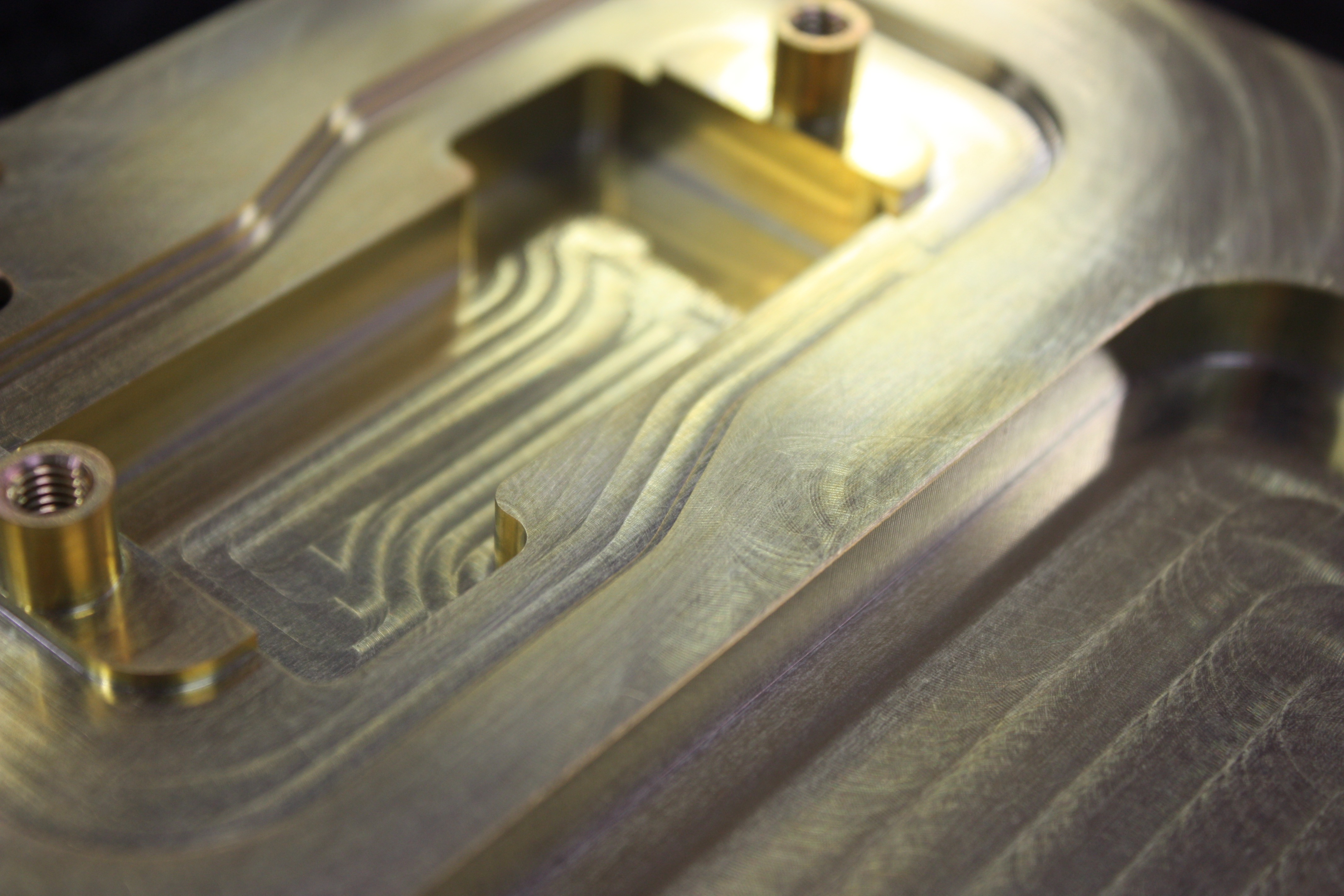
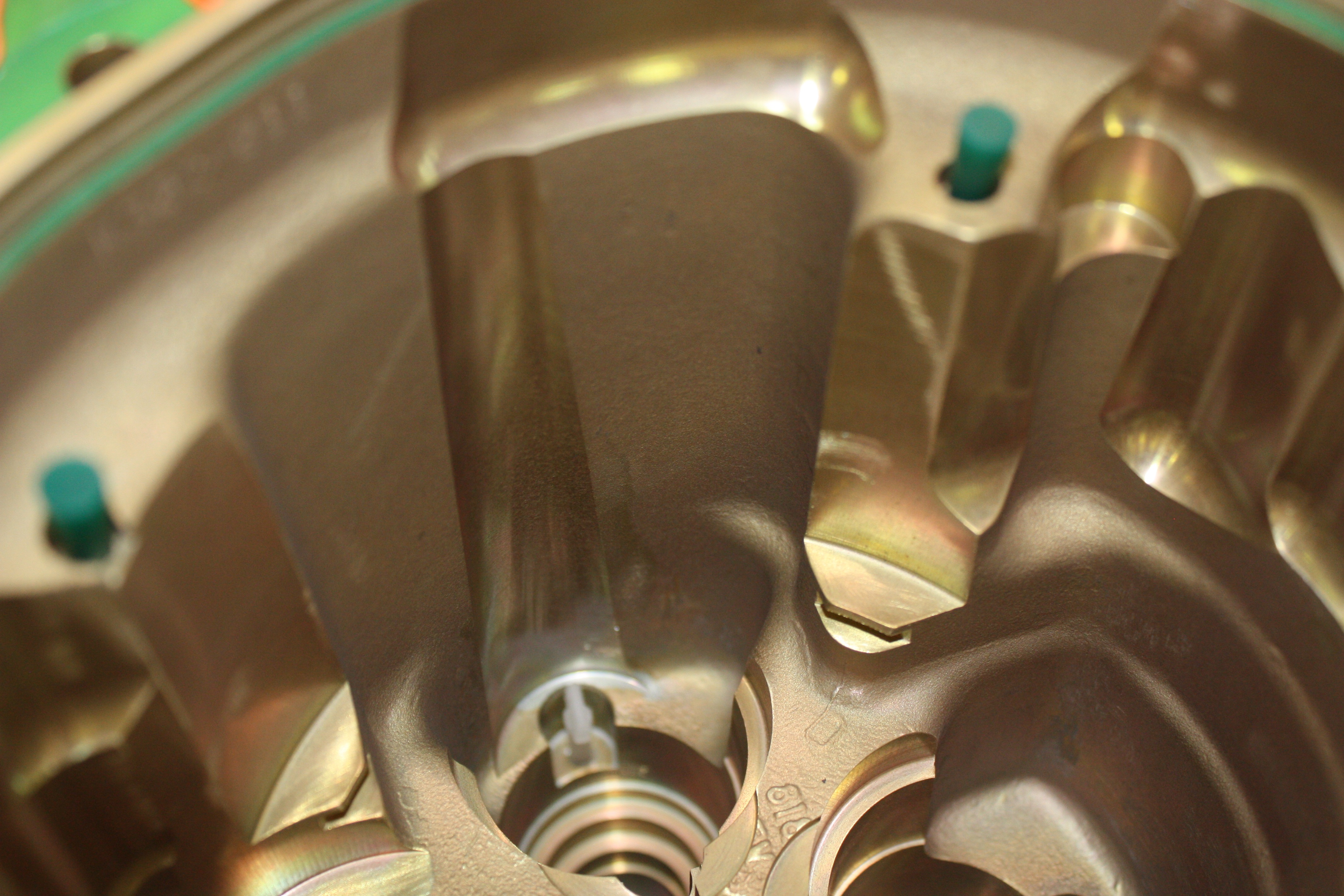


Chemfilm
Chemfilm is a chromate conversion coating for aluminum and its alloys that creates a protective finish on the surface of the metal. Since there is no growth associated with this conversion, the dimensions of the part remain virtually unchanged after processing. This treatment also changes the surface properties of the aluminum making it less susceptible to corrosion and more compatible with paints, powder coatings, and other finishing processes. Chemfilm is also commonly referred to as Chemical Film, Chromating, Alodine, and Iridite.
- Corrosion resistance
- Paint adhesion
- No dimensional impact
- Electrically conductive
For more chemical film information
Specifications
Class 3: Higher electrical conductivity
Type 1: Contains hexavalent chromium – Clear or yellow coating
Type 2: Does not contain hexavalent chromium (RoHS compliant) – Clear coating only
Class 3: Higher electrical conductivity
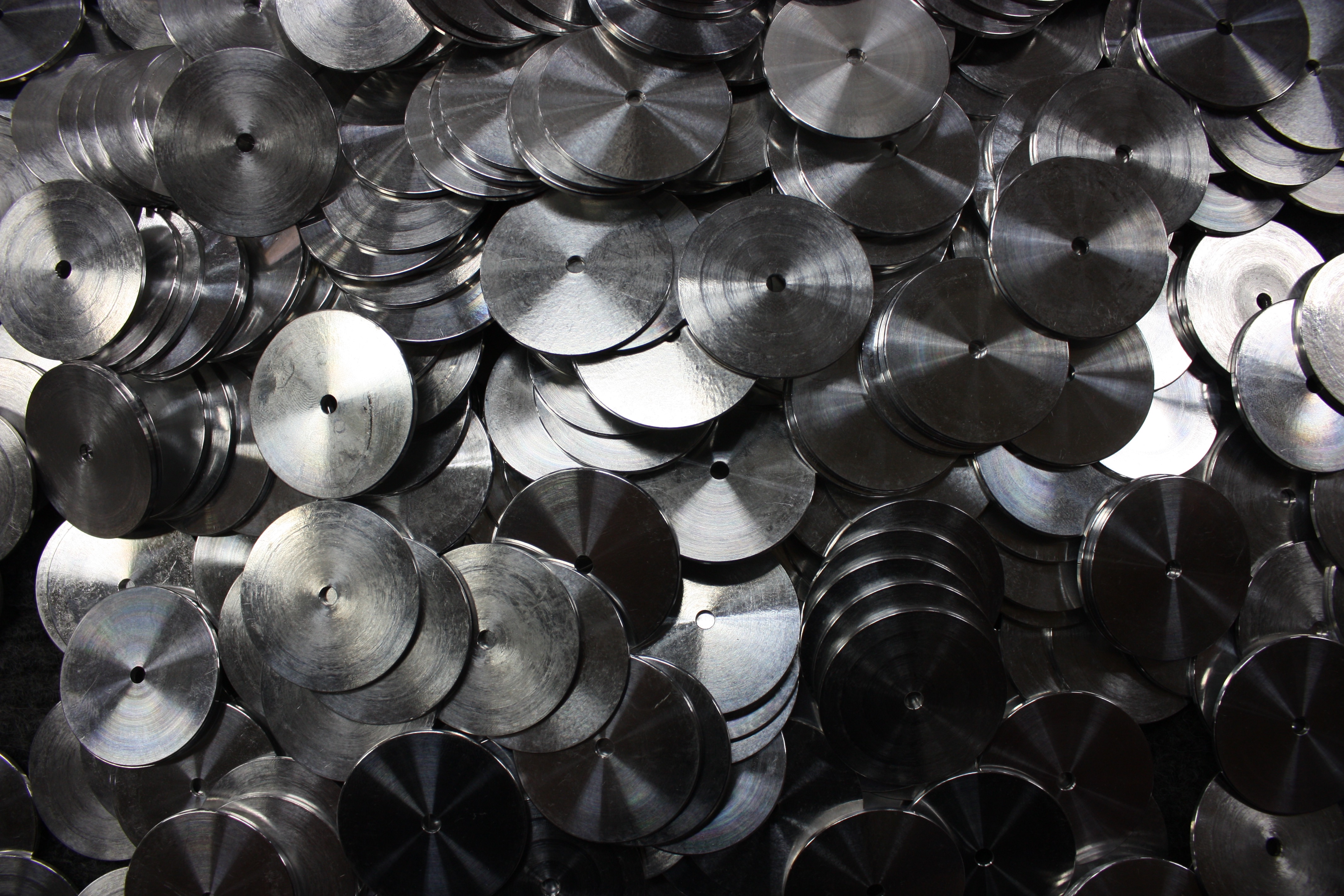
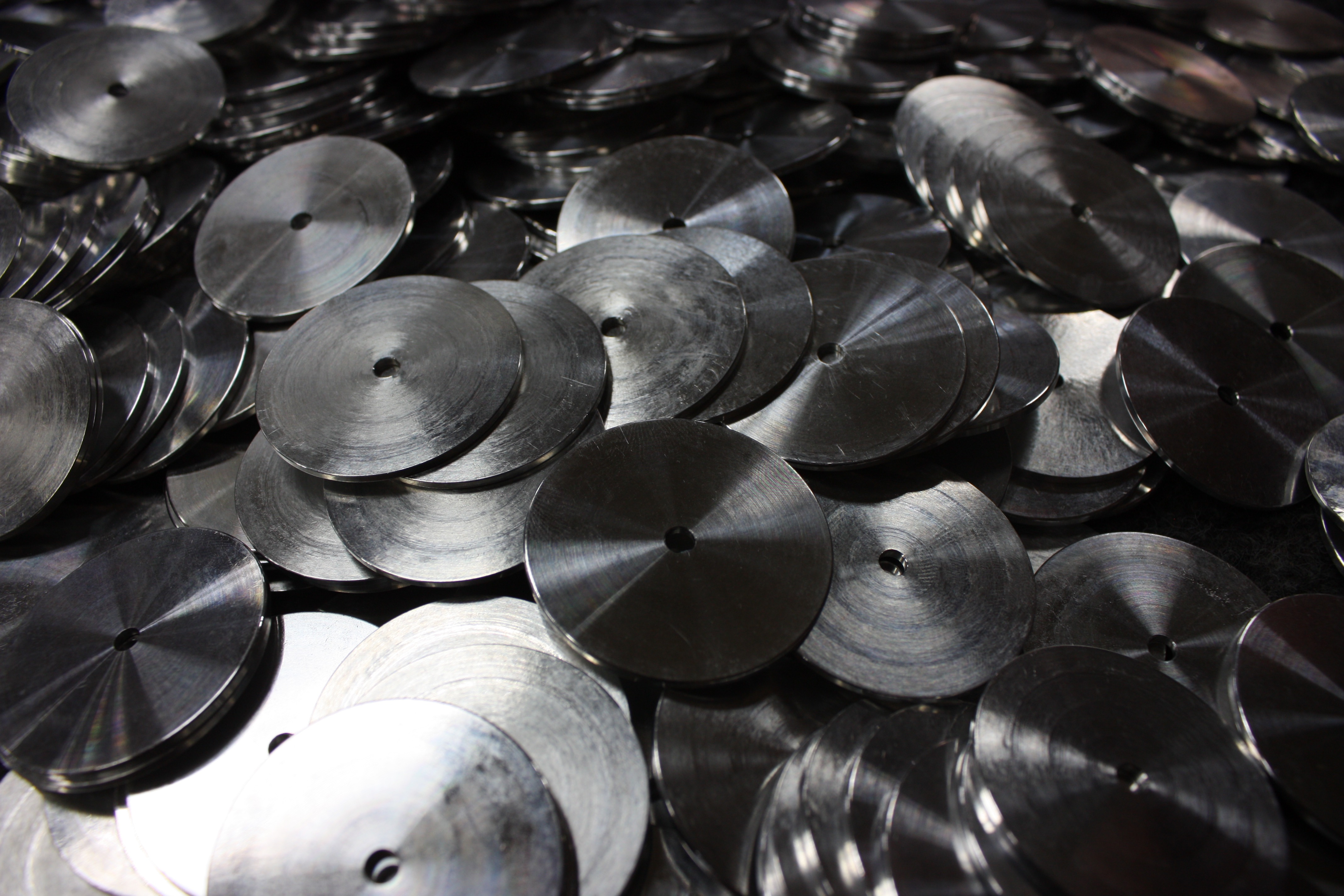


Passivation
Passivation is the process of removing iron and other surface contaminants from stainless steel materials. It also can help repair any damaged areas in the protective chromium oxide layer by facilitating its oxidation. Additions of strong oxidizers, such as sodium dichromate, can further accelerate oxide formation. Passivation ensures that the surface is free from corrosion, which can negatively affect the life and properties of stainless steel materials.
- Corrosion resistance
For more passivation information
Specifications
Method 1: Passivation in Nitric Acid
Method 2: Passivation in Citric Acid
Type 2: Medium Temperature Nitric Acid with Sodium Dichromate
Type 3: High Temperature Nitric Acid with Sodium Dichromate
Type 6: Low Temperature Nitric Acid
Type 7: Medium Temperature Nitric Acid
Code G
Code H
Code I
Code J
Code N
Nitric 2
Nitric 3
Citric 1
Citric 2
Citric 3
Citric 4
Type VI: Low temperature nitric acid solution
Type VII: Medium temperature nitric acid solution
